what orbitals overlap to form the c-c bond in chch?
Science > Chemistry > Physical Chemistry > Nature of Chemical Bail > Overlapping of Orbitals
In this article, we shall study the germination of bonds past overlapping of orbitals and different types of overlaps.
Germination of Hydrogen Molecule on The Basis Of Orbital Overlap:
The electronic configuration of a hydrogen cantlet is 1s1. Information technology contains one unpaired electron in its valence shell. Therefore 1s orbital in the hydrogen atom is bonding orbital. When the two hydrogen atoms having valence electrons with opposite spins approach each other, the attractive force dominates the repulsive force between the electrons in the initial stage. Thus, as the distance between two hydrogen atoms decreases the potential energy of the organisation gradually decreases.
A country of minimum potential energy is reached when the forces of allure are balanced past the forces of repulsion between two hydrogen atoms. At this point the energy of the arrangement is minimum and the stability is maximum. At this phase orbital of 2 hydrogen atoms, overlap and spins of electrons are neutralized and a stable covalent bond is formed between hydrogen atoms, forming H2, molecule. In this case, the overlap of orbitals is maximum. This overlap is called s-s overlap and bond formed are coaxial overlapping of 2 s orbital is called southward-s sigma (σ) bond.
In the formation of a molecule, the release of free energy comes from 2 sources. The neutralization of spin magnetic moments of the ii electrons and the accumulation of electron density betwixt 2 nuclei.
Diagram :
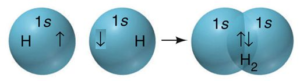
ane S Orbital one S Orbital S-S overlap
Reason: Helium does not form a diatomic molecule:
Helium with atomic number two has electron configuration 1s2. Thus helium contains 2 paired electrons in its 1s orbital. The pairing of electrons in 1s orbital neutralizes the spin magnetic moments of each other. This gives stability to the helium cantlet. At that place are no empty orbitals in the first beat for unpairing and promoting these paired electrons to higher energy orbital. Thus helium has no unpaired electron i.e. no bonding orbital. Therefore according to valence bond theory, it cannot grade a covalent bond with another helium atom.
Each helium atom has paired electrons in 1s is orbital. If two such orbitals come up close to each other, in that location is net repulsion betwixt them because repulsive forces are stronger than the attractive forces. If they do so it increases the potential energy of the arrangement and it becomes unstable. Thus overlapping of orbitals cannot take place. Therefore helium cannot form a diatomic molecule. It exists as a monoatomic gas.
Types of Overlap of Atomic Orbitals:
The term overlap refers to the overlap of the atomic orbitals of the two budgeted atoms as they enter into the bail formation stage. In the example of south and p orbitals, there tin be three types of overlap.
southward – s orbital overlap ( formation of H2molecule):
The common overlap betwixt the half-filled s orbitals of ii atoms is called s – south overlap and the covalent bail formed is known as sigma (s) bond. east.m. formation of a hydrogen molecule from two hydrogen atoms.
southward – orbital is spherical in shape and overlapping takes place to some extent in all directions. Hence southward -southward bond is not – directional.
Hydrogen (1s1) cantlet has 1s orbital containing a single electron i.east. it is one-half-filled. Two such 1s orbitals from the two hydrogen atoms having electrons with contrary spins approach each other, then the potential energy of the system decreases. The two 'southward' orbitals overlap each other when they acquire minimum potential energy, forming H-H sigma bond or s-south overlap. H-H bond is a nonpolar covalent bond.
As the 2 orbitals are overlapping such that the overlapped region lies on the line joining the two nuclei of the overlapping orbitals (centric overlapping) bond formed is sigma bond.
Diagram :

1 S Orbital ane South Orbital S-S overlap
p – p orbital overlap (Germination of Fluorine F 2 molecule):
The mutual overlap between two half-filled p – orbitals of ii atoms is called p – p overlap and the covalent bail formed is known as p – p bond. If the overlapping takes place along the internuclear axis the bond is called sigma bond and if the overlapping takes place literally the bond is known as pi bond. east.g. formation of fluorine molecule from two fluorine atoms. CI2, Br2and Itwo are also formed by p – p overlap.
The atomic number of fluorine is 9. The electronic configuration of the fluorine atom is 1s2. 2s2. 2px ii, 2py 2, 2pz 1. Each F cantlet has one unpaired electron in p – orbital (pz orbital). When two fluorine atoms each containing unpaired electron with contrary spins approach each other, then the potential free energy of the system decreases. The two 'p' orbitals overlap each other when they learn minimum potential energy.
As the 2 orbitals are overlapping such that the overlapped region lies on the line joining the two nuclei of the overlapping orbitals (centric overlapping) bond formed is sigma bail. Equally p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped they overlap in a item management. Therefore the p-p bail is directional. The back lobe of the overlapping p orbital is distorted and its size is reduced. This is due to the tendency of the electron to remain in the overlapping region.
F-F bond is a non-polar, equally shared pair of electrons is attracted by both the atoms.
Diagram :

ane P Orbital 1 P Orbital P-P overlap
southward – p orbital overlap (Formation of Hydrogen Fluoride Molecule):
The overlap betwixt the half-filled south – orbital of one cantlet and the half-filled p – orbital of some other atom is called s – p overlap and the covalent bond formed is known as s – p sigma bond. Eastward.g.: Formation of HF molecule, H – Ten bond in HCI, HBr, and Hullo are likewise formed by due south-p overlap.
The electronic configuration of a hydrogen atom is 1s1, while that of fluorine atom is 1s2. 2s2. 2px2, 2py2, 2pz1. Thus 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom and the 2p orbital of fluorine cantlet containing unpaired electron tin overlap and the bond formation is possible provided the spin of electrons in overlapping orbitals is opposite. The bond in hydrogen fluoride is a s – p bond. Equally the 2 orbitals are overlapping such that the overlapped region lies on the line joining the ii nuclei of the overlapping orbitals (axial overlapping) bond formed is sigma bond. The back lobe of the overlapping p orbital is distorted and its size is reduced. This is due to the tendency of the electron to remain in the overlapping region.
Fluorine is more than electronegative than hydrogen, hence H-F bail is polar.
Diagram :

Reason: H – F bond is polar.
HF molecule is formed by the southward-p overlap of orbitals. On Pauling scale, the electronegativity of H is ii.1 and that of F is 4. Thus fluorine is more electronegative than H, the electronic cloud in this bond is displaced more towards fluorine. In other words, the electron pair shared betwixt the two atoms is attracted more towards fluorine. This gives fluorine atom a partial negative accuse (δ -) and hydrogen cantlet a partial accuse (δ +).
Thus the H – F bond is not purely covalent. It possesses a partial ionic grapheme and is said to be a polar bond. The bail has 43% ionic character. H – X bond in HCI, HBr, and How-do-you-do are besides polar since CI, Br and I are more electronegative than H.
Science > Chemical science > Physical Chemistry > Nature of Chemical Bail > Overlapping of Orbitals
freemanbrourcomis.blogspot.com
Source: https://thefactfactor.com/facts/pure_science/chemistry/physical-chemistry/overlapping-of-orbitals/10964/
0 Response to "what orbitals overlap to form the c-c bond in chch?"
Post a Comment